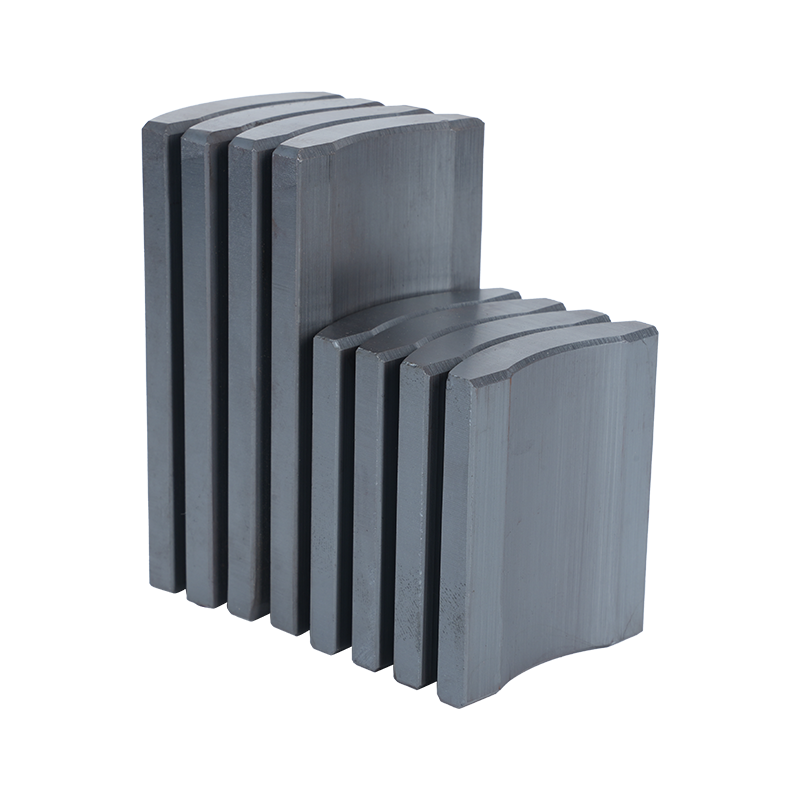
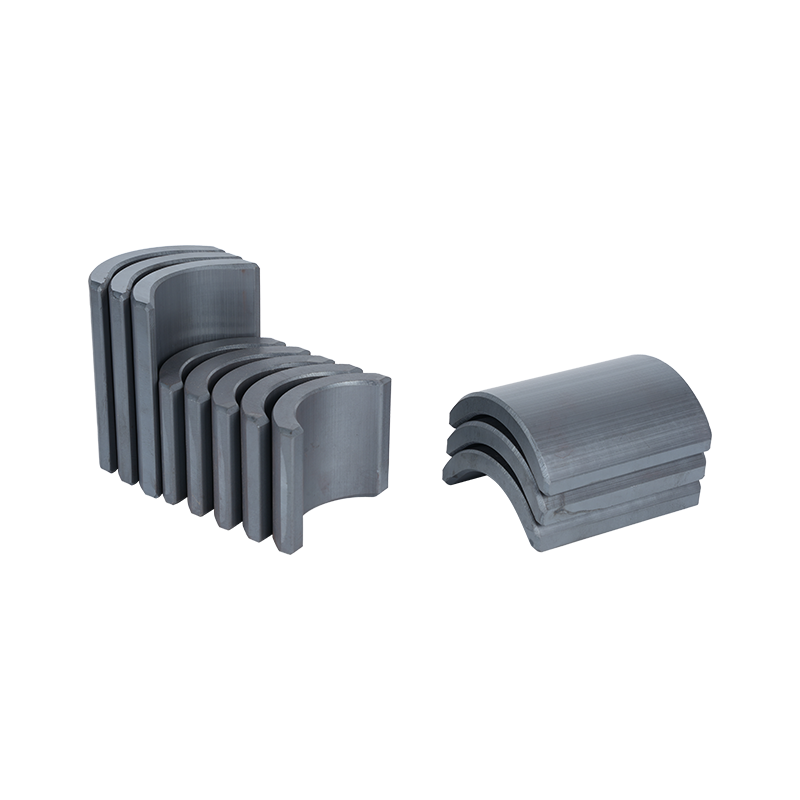
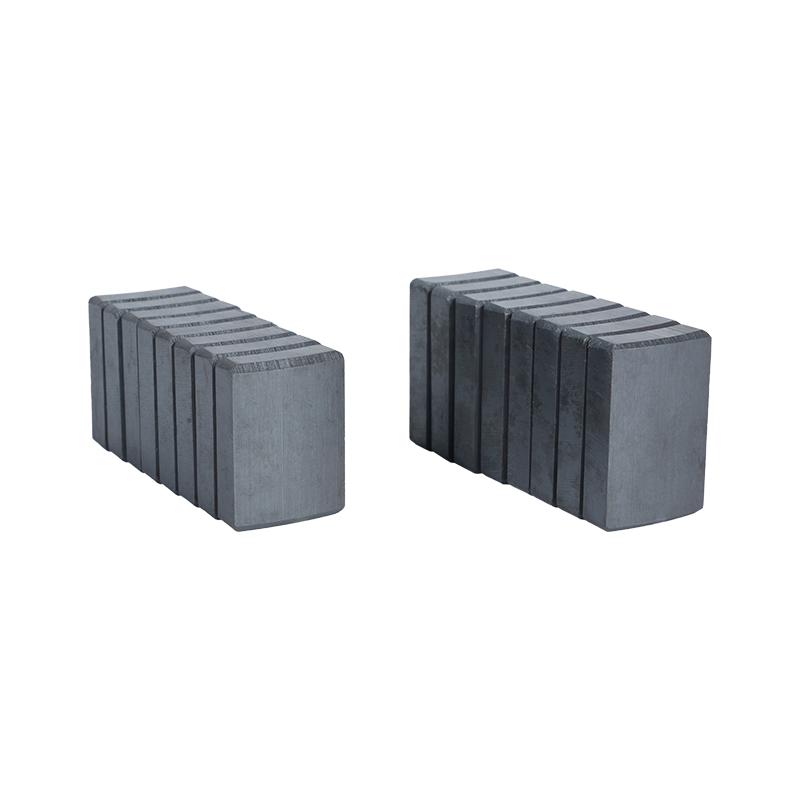
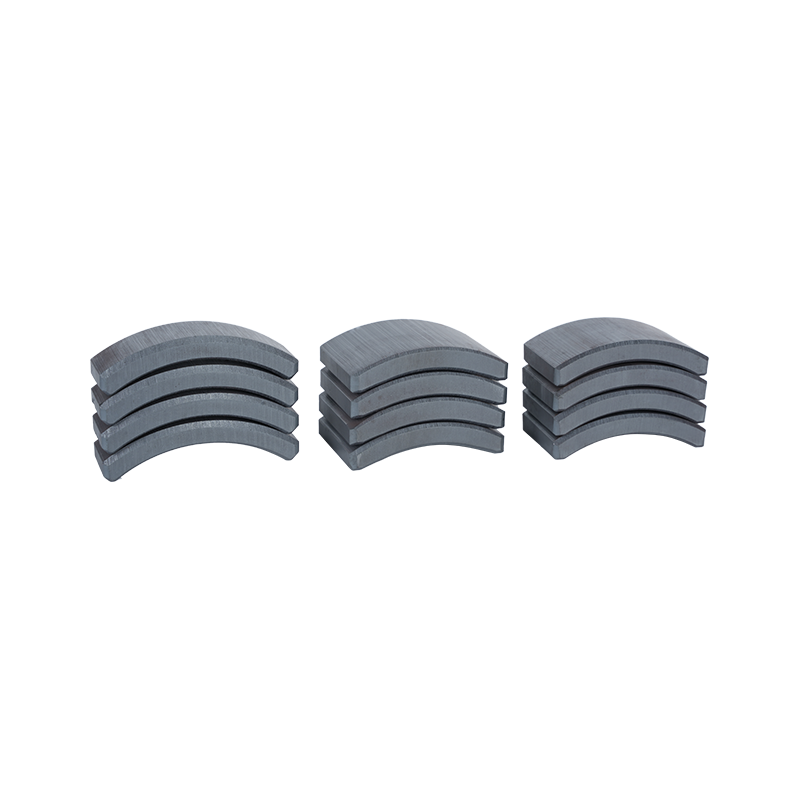
Dong Yang TianQi Magnetic Segment Co.,Ltd.(formerly Shuangyang Magnet Tile) is a professional enterprise specializing in the production of motor magnet tiles
Search by posts
Categories
Popular products
Contact Us
Industry News
 By Admin
By Admin
Permanent Magnetic Ferrite Unlocking Industrial Efficiency and Technological Potential
Permanent magnetic ferrite has established itself as an essential material in the field of industrial magnetics.Factories focus on improving production speed, reducing operational costs, and maintaining steady performance, and ferrite provides a practical solution for meeting these demands. Its stable properties and scalability make it suitable for both high‑volume industrial lines and technical applications that require reliable magnetic performance.

Permanent Magnetic Ferrite Factory Efficiency
From a factory perspective, production of permanent magnetic ferrite magnets shows measurable gains in efficiency. Production typically starts with calcining mixtures of iron oxide and strontium carbonate, then grinding to particles smaller than 2 µm to ensure a uniform magnetic domain structure. Because ferrite uses abundant raw materials and established sintering techniques, manufacturers report reduced per‑unit production cost compared to rare‑earth alternatives. In practical terms, this translates into shorter processing hours per unit, reduced scrap rates, and manageable tool wear.
Permanent Magnetic Ferrite Technology
From a technological viewpoint, permanent magnetic ferrite continues to evolve. Compared to neodymium magnets, ferrite magnets trade peak strength for stability. They offer high resistance to demagnetization and corrosion, and typical grades have Curie temperatures around 450–460 °C. Hard ferrite magnets account for a significant portion of permanent magnet production by weight, enabling engineers to rely on large volumes, consistent quality, and scalable batch processing.
Permanent Magnetic Ferrite Quality and Positive Outcomes
In industrial settings, permanent magnetic ferrite is recognized for its combination of durability, stability, and cost efficiency. Its ceramic‑based oxide structure provides strong resistance to corrosion, heat, and demagnetization, making it suitable for environments with high humidity, temperature fluctuations, or continuous mechanical stress. Production lines that rely on ferrite magnets report lower rates of replacement and maintenance, which translates into reduced operational interruptions and better overall productivity.
Applications span a wide range of devices: in electric motors, ferrite magnets maintain consistent torque output over tens of thousands of operational hours; in actuators and sensors, they ensure precise positioning and reliable signal consistency; in loudspeakers, ferrite supports stable sound quality even under prolonged usage.
Market trends confirm the material’s industrial value. Production volumes and adoption rates for ferrite magnets show steady growth, reflecting its practical advantages and strong feedback from manufacturers who prioritize efficiency, scalability, and long-term reliability. The balance between moderate magnetic strength and high durability positions permanent magnetic ferrite as a trusted choice for large-scale manufacturing and engineering applications.
Permanent Magnetic Ferrite Versus Alternative Magnet Materials
How does permanent magnetic ferrite compare with other magnets? Rare‑earth magnets such as Nd‑Fe‑B provide higher magnetic energy products, suitable for compact applications. However, the cost, supply chain complexity, and coating requirements of rare‑earth magnets often make ferrite the preferred choice for high-volume industrial production.This makes ferrite an effective solution for bulk applications, such as motors, loudspeakers, and consumer appliances, while higher-performance magnets are reserved for specialized tasks.
Future Outlook for Permanent Magnetic Ferrite
Industries focusing on electric motors, consumer electronics, and renewable energy increasingly rely on magnetic materials that offer both stability and cost efficiency. Factories are presented with opportunities to enhance processing efficiency, improve yield, and extend the service life of ferrite magnets, creating a balance between technological performance and practical industrial use.
Ultimately, permanent magnetic ferrite extends beyond being a simple cost-saving option. It represents a deliberate production strategy that integrates operational efficiency, technological advancement, and consistent reliability.